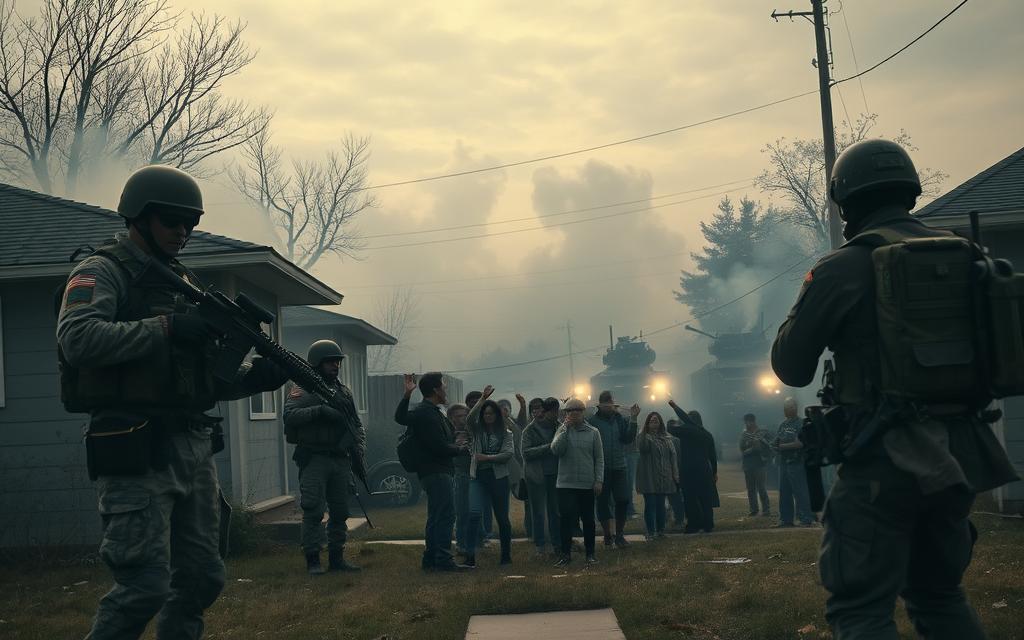
The abrupt shift from civil liberties to military-enforced restrictions demands immediate adaptation. Historical precedents, such as Hawaii’s three-year governance under martial law during WWII, demonstrate how quickly civilian order can dissolve. This transformation introduces curfews, restricted movement zones, and mandatory compliance with armed forces – realities requiring proactive household planning.
Securing your residence becomes paramount. Reinforced entry points and discreet resource stockpiles – including water filters and non-perishables – form the foundation of domestic safety. Families should establish rendezvous protocols and synchronise schedules to avoid curfew violations, as outlined in our analysis of historical martial law implementations.
Public conduct during such periods requires meticulous discretion. Neutral attire, minimal digital footprints, and avoidance of crowded areas reduce visibility to patrols. Preparation isn’t paranoia – it’s practical resilience against potential supply chain disruptions and communication blackouts.
This guide prioritises tangible safeguards over speculative fears. From creating secondary medical caches to understanding local emergency protocols, we focus on actionable measures that maintain family security without compromising ethical standards. The subsequent sections detail specific strategies for sustaining autonomy when civil protections lapse.
Understanding Martial Law: Definition and Context
Legal frameworks shape how societies respond to crises, yet few concepts carry as much weight as martial law. Unlike standard emergency protocols, this governance model transfers power from elected bodies to armed forces. The absence of a concrete constitutional definition in nations like the UK creates ambiguity, heightening the need for public awareness.
Defining Military and Civil Order
Martial law replaces civilian legal structures with military tribunals and regulations. While natural disasters might involve troops assisting local authorities, full implementation dissolves parliamentary oversight. Constitutional safeguards like habeas corpus often vanish, replaced by curfews and warrantless searches.
In the United States, Supreme Court rulings have historically limited martial law’s scope, yet its precise boundaries remain contested. British legal scholars emphasise its rarity in modern democracies, noting the Civil Contingencies Act 2004 prioritises temporary emergency powers over permanent military rule.
International and National Perspectives
Global approaches vary starkly. Thailand’s 2014 coup saw soldiers assume legislative roles, while France maintains strict separation between military and civil crises. The UK’s framework permits temporary military aid during terrorist incidents without suspending civilian law entirely.
“Martial law isn’t merely soldiers on streets – it’s the systematic replacement of justice systems with battlefield logic.”
This distinction proves vital. Recognising when governance crosses from emergency support to authoritarian control enables informed responses. Families should monitor whether local councils retain decision-making powers or defer completely to uniformed authorities.
A Historical Overview of Martial Law in the United States
From labour disputes to wartime emergencies, military governance has reshaped American society 68 times since 1812. The Brennan Centre for Justice notes over half these cases addressed industrial conflicts, with courts frequently questioning their legality. This pattern reveals how crises test constitutional boundaries.
Key Historical Instances
Andrew Jackson’s 1812 New Orleans deployment set early precedents. His arrest of a critical journalist led to congressional fines – a rare check on executive power. Abraham Lincoln later suspended habeas corpus during the Civil War, prioritising union preservation over civil liberties.
Franklin Roosevelt’s administration expanded military authority during WWII. Hawaii endured nearly three years under strict controls, while Japanese-Americans faced forced internment. The 1960s saw urban deployments in San Francisco and Detroit amid racial tensions.
| Year | Location | Cause | Duration | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1812 | New Orleans | War preparedness | 4 months | Supreme Court rebuke |
| 1861-1865 | Border states | Civil War unrest | 4 years | Contested legality |
| 1941-1944 | Hawaii | WWII security | 34 months | Mass surveillance |
| 1963 | Detroit | Civil rights protests | 1 week | National Guard withdrawal |
Lessons from Past Declarations
Historical data shows 33 legal challenges to military governance, with judges often ruling against overreach. Labour strikes triggered 29 deployments, proving economic stability drives governmental responses. Lasting three years in Hawaii, the longest instance demonstrates how emergencies justify extended controls.
Modern precedents suggest temporary measures face stricter scrutiny. As one constitutional scholar observed: “Each declaration chips away at judicial patience for militarised solutions.” These patterns emphasise the need for balanced crisis responses.
How Martial Law Impacts Civil Liberties and Daily Life
Civil liberties undergo radical transformation when military authority supersedes civilian governance. Overnight, fundamental freedoms dissolve as armed forces implement controls prioritising order over individual autonomy. This seismic shift affects everything from morning commutes to private conversations.
Changes to Freedom of Movement and Expression
Curfews and checkpoints become standard under military rule. Civilians might require travel permits for basic errands, with unauthorised journeys risking detention. Expression faces harsh suppression – a sarcastic remark about law enforcement could warrant interrogation.
Public gatherings vanish overnight. Peaceful protests morph into criminal acts, with participants facing military tribunals. Even digital communications face scrutiny, as seen during Thailand’s 2014 coup where social media criticism led to arrests.
Impact on Civil Rights and Legal Protections
Habeas corpus protections typically evaporate, enabling indefinite detention without charge. Civil courts lose jurisdiction, leaving citizens subject to military justice systems. Privacy rights collapse as soldiers gain entry rights to homes without warrants.
Essential services become conditional. Hospitals might prioritise military personnel, while supermarkets operate under rationing systems. The constitution’s safeguards against property seizures often hold no weight, with authorities requisitioning supplies for “public safety”.
These transformations create societal fractures. As observed during the UK’s 2000 fuel protests, even temporary military involvement alters community dynamics. Preparedness now centres on adapting to restricted freedoms while maintaining ethical boundaries.
Clear Guidance: what to do if martial law is declared
Swift implementation of military governance creates immediate logistical challenges for households. Prioritise retrieving family members within 90 minutes of announcement – delayed reunions risk permanent separation under movement restrictions. Every vehicle requires 72-hour survival kits containing:
- Water purification tablets and calorie-dense rations
- Compact trauma dressings and tourniquets
- Paper maps with pre-marked alternative routes
Conceal surplus supplies using diversion safes and dispersed storage. When military personnel establish neighbourhood checkpoints, visible stockpiles become vulnerable to requisitioning. Resource camouflage proves critical – repurpose everyday containers for discreet caching.
Communication systems require redundancy. Battery-powered radios with pre-set emergency frequencies circumvent mobile network shutdowns. Establish rally points beyond primary residences, like trusted community centres or rural landmarks.
Compliance without cooperation defines optimal interactions. Answer patrols’ questions briefly, avoiding volunteered information. Memorise legal parameters of military governance to recognise overreach while maintaining non-confrontational demeanour.
The Role of Government and Military in Declaring Martial Law
Governmental hierarchies dictate the implementation of military governance during extreme crises. Constitutional frameworks establish a precise chain of command, with executive authority expanding dramatically when civil order collapses. This power structure determines whether local commanders or national leaders initiate martial measures.
Executive Authority and Legal Frameworks
Federal declarations typically follow the Insurrection Act of 1807, permitting troop deployment to suppress rebellions. State governors wield similar powers through emergency clauses in their constitutions – unless explicitly restricted. Recent Supreme Court rulings have reshaped these dynamics, granting broader immunity for executive actions deemed “official”.
| Authority Level | Legal Basis | Troop Deployment Limits | Oversight Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal | Insurrection Act | Unlimited | Congressional review |
| State | Emergency Powers Acts | National Guard only | State legislature |
| Local Military | Immediate Threat Doctrine | 48-hour window | Federal authorisation |
Local and State Government Involvement
Regional leaders face complex choices when crises escalate. While some states require legislative approval for martial law declarations, others grant unilateral gubernatorial authority. Coordination between civilian officials and military commanders often determines whether local governance survives the transition.
“The 2024 immunity ruling created a constitutional grey area – presidents now operate with reduced accountability during emergency actions.”
Resource allocation becomes contentious during joint operations. Military commanders typically control supply distribution, while civilian authorities handle public communications. This uneasy partnership underscores the fragility of civil-military relations under martial governance.
Distinguishing Martial Law from a State of Emergency
Understanding governance hierarchies becomes critical when distinguishing emergency protocols from full military control. While both scenarios involve heightened security measures, their operational frameworks differ fundamentally. Civilian oversight remains intact during most crises, with armed forces playing supportive roles rather than assuming command.
Key Differences in Enforcement
Emergency declarations typically deploy civilian law enforcement alongside National Guard units under local authority. Curfews or travel restrictions apply temporarily, often with parliamentary oversight. In contrast, martial rule replaces police with combat-trained personnel answerable only to military tribunals.
| Aspect | State of Emergency | Martial Law |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Civilian authorities | Military command |
| Legal oversight | Active judicial review | Suspended |
| Enforcement | Police and National Guard | Active-duty troops |
| Rights suspension | Partial | Complete |
| Duration | Time-limited | Indefinite |
Implications for Civilian Preparedness
Households must adapt strategies based on the crisis level. Emergency scenarios allow stockpiling essentials openly, while military governance necessitates discreet resource storage. Legal recourse disappears under martial rule – understanding local emergency legislation helps identify governance thresholds.
Recent pandemic responses demonstrate emergency measures’ scope: restricted gatherings without suspending courts. Compare this to the 1944 Hawaiian model where military governors controlled mail and commerce. Preparedness plans should address both short-term compliance and long-term autonomy preservation.
Preparing Your Home and Family for Potential Martial Law
Proactive household coordination forms the bedrock of resilience during governance upheavals. Families must establish protocols before restrictions immobilise communities, as military-enforced curfews often leave minimal preparation time.
Creating a Family Safety Plan
Designate primary and secondary rally points within walking distance of key locations. Consider accessible landmarks unaffected by potential military roadblocks – libraries or religious centres often remain operational during crises.
Essential planning elements include:
- Synchronised check-in times using analogue clocks
- Water reserves for 14 days per person
- Pre-arranged signals for safe-house transitions
Households with vulnerable members require tailored strategies. Elderly relatives might need emergency medical packs, while children benefit from simplified instruction cards. Document all plans using weatherproof materials stored in multiple locations.
“Families that rehearse emergency scenarios reduce decision-making panic by 73% during actual crises.”
Assign clear roles during weekly drills: who secures entry points, monitors supplies, or handles communications. Rotate responsibilities to prevent skill gaps. Psychological readiness proves equally vital – discuss potential restrictions openly while emphasising collective adaptability.
Maintain discreet travel kits containing local maps and contingency funds. When military checkpoints emerge, swift reunification depends on pre-planned alternative routes avoiding major thoroughfares.
Emergency Supplies and Prepping Techniques
Strategic resource management becomes critical when civilian protections diminish. Discreet storage solutions prevent requisitioning by authorities while ensuring family resilience. Prioritise off-site caches over centralised stockpiles – secondary locations reduce vulnerability during property searches.
Food, Water and Medical Caches
Distribute essentials across multiple hidden compartments. Vacuum-sealed dry goods in false wall cavities maintain freshness without attracting attention. Water reserves require rotation every six months – pair purification tablets with collapsible containers for space efficiency.
Medical stocks need dual storage: accessible first-aid kits and concealed trauma supplies. Include haemostatic gauze and broad-spectrum antibiotics. Rotate prescriptions discreetly, using generic labelling to avoid scrutiny.
Protective Equipment and Communication Devices
CBRN-rated masks like the MIRA CM-6M with NATO-certified filters offer chemical threat protection. Store these alongside compact Geiger counters in grab-and-go pouches. Level IIIa ballistic helmets provide impact resistance without excessive weight.
Maintain analogue communication backups. Wind-up radios with pre-set emergency frequencies bypass network shutdowns. Encrypted messaging apps on Faraday pouch-protected devices ensure temporary secure contact when digital systems remain operational.
Preparation balances practicality with invisibility. By integrating these measures into daily routines, households sustain autonomy during prolonged restrictions without compromising safety protocols.